Have you ever wondered how companies reward their employees beyond just a paycheck? Stock-based compensation might be the answer.
It’s a powerful tool that can boost your earnings and make you feel like a true part of the company’s success. But what exactly is stock-based compensation, and how does it affect your financial future? Keep reading to discover how this type of pay works, why it matters to you, and what you need to know to make smart decisions about your career and investments.
Credit: einvestingforbeginners.com
Basics Of Stock-based Compensation
Stock-based compensation is a way companies pay employees using company shares. This method rewards workers and helps companies keep talent. It ties employee success to company success.
Understanding the basics helps you see how it works. It involves different types of stock awards. Each type has unique features and benefits.
Types Of Stock-based Awards
Companies use several stock awards to compensate employees. Common types include stock options, restricted stock units, and stock grants. Each type offers different rights and benefits. Stock options give the choice to buy shares later. Restricted stock units are shares given after some time. Stock grants are shares given immediately.
How Stock Options Work
Stock options give employees the right to buy shares at a set price. The price is fixed when options are granted. Employees can buy shares after a waiting period called vesting. If the share price rises, employees can buy at the lower price. They can sell shares to make a profit. If prices fall, employees may not use their options.
Restricted Stock Units Explained
Restricted stock units (RSUs) are company shares given to employees later. Employees do not own the shares until they vest. Vesting happens after working for a set time or meeting goals. Once vested, employees own the shares and can sell them. RSUs provide value even if the stock price changes. They encourage employees to stay longer with the company.

Credit: eqvista.com
Reasons Companies Use Stock-based Pay
Companies use stock-based pay for several important reasons. It helps them attract skilled workers, keep employees motivated, and align goals with shareholders. Stock-based compensation offers benefits beyond regular salary payments. It creates a sense of ownership among employees. This approach supports long-term success for both the company and its staff.
Attracting Talent
Offering stock-based pay makes a job more appealing. Many talented candidates prefer companies that share ownership. It shows that the company values its employees. This type of pay can compete with higher salaries elsewhere. Startups and tech firms often use stock options to attract skilled workers. It helps them stand out in a crowded job market.
Motivating Employees
Stock-based compensation encourages employees to work harder. When their pay depends on company success, motivation grows. Employees feel responsible for the company’s future. This can increase productivity and focus. It also helps reduce turnover. Workers tend to stay longer to see their stocks grow in value.
Aligning Interests With Shareholders
Stock pay aligns employee goals with those of shareholders. Both groups want the company’s value to rise. Employees become more aware of company performance. They think like owners, not just workers. This alignment helps drive better decisions. It creates a stronger connection between staff and investors.
Accounting For Stock-based Compensation
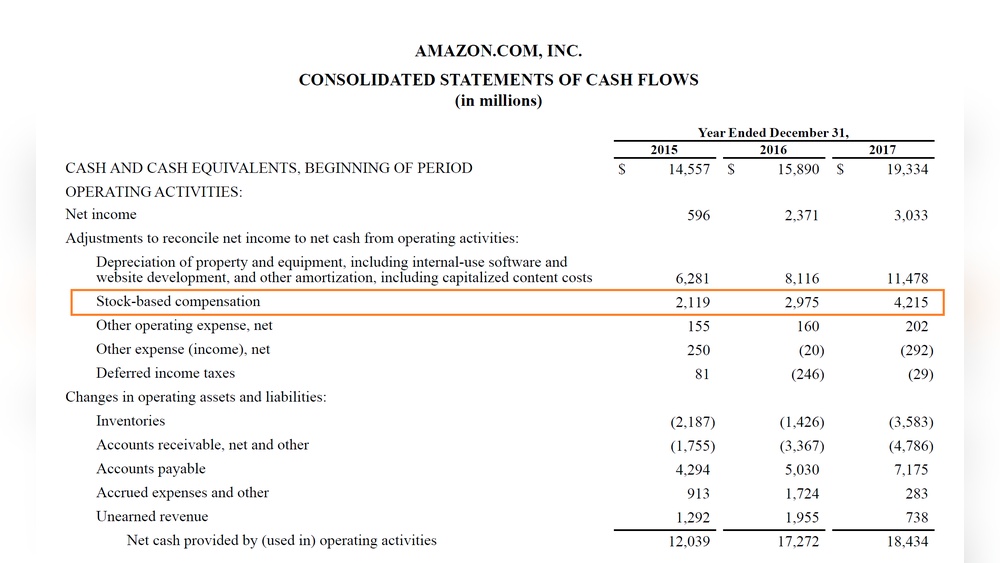
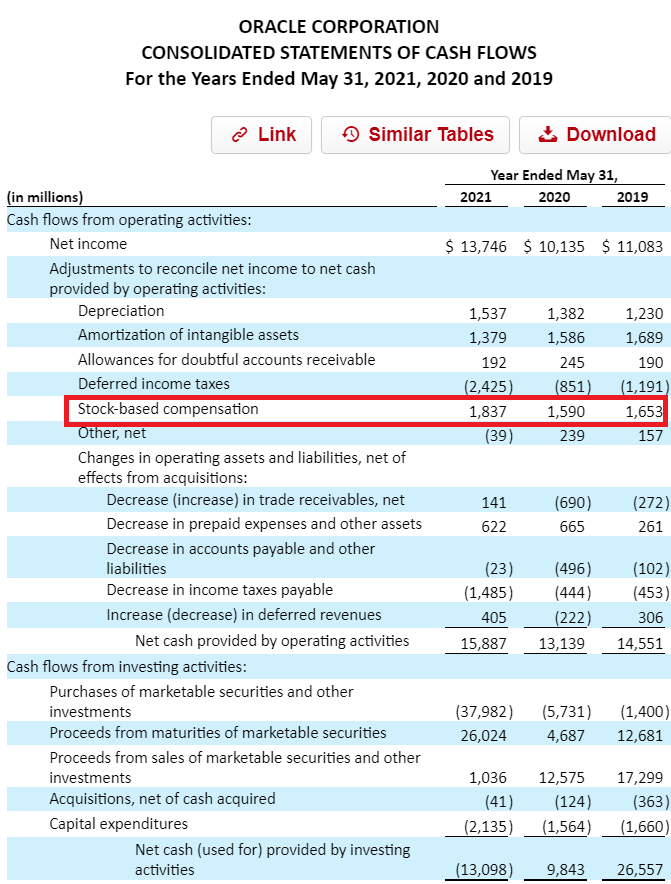
Accounting for stock-based compensation is a key part of understanding company finances. It shows how businesses record the cost of giving employees shares or stock options. This process helps investors and others see the true value of employee pay.
Companies must follow rules to report these costs clearly. These rules make sure all businesses treat stock compensation the same way. This section explains how companies recognize expenses, show the impact on financial statements, and handle tax matters.
Recognizing Expenses
Companies record stock-based compensation as an expense. This happens over the time employees earn their shares or options. The expense matches the fair value of the stock or option at the grant date. Spreading the cost over time reflects the employee’s service period. This method ensures expenses are reported fairly and consistently.
Impact On Financial Statements
Stock compensation affects both the income statement and the balance sheet. The expense reduces net income, showing a real cost of employee pay. On the balance sheet, companies add to equity when employees receive shares. This changes the ownership structure but does not use cash. Financial statements show the full picture of company costs and equity changes.
Tax Considerations
Tax rules for stock compensation vary by country and type. Companies may get tax deductions when employees exercise options or sell shares. Employees might owe taxes on the value of shares they receive. Proper accounting helps companies and employees meet tax laws and avoid surprises. Understanding these tax rules is important for both sides.
Benefits And Drawbacks
Stock-based compensation offers various benefits and drawbacks. It can motivate employees and align their interests with the company. At the same time, it carries risks and can affect company performance. Understanding these aspects helps employees and employers make better decisions.
Advantages For Employees
Stock-based compensation gives employees a chance to own part of the company. It can increase their total pay beyond just salary. Employees may benefit from stock price growth over time. It encourages long-term commitment and loyalty. This type of pay can also offer tax advantages in some cases.
Risks And Downsides
The value of stock-based pay can go down as well as up. Employees may end up with less money if stock prices fall. It can create uncertainty about total income. Some employees might feel pressured to stay with the company longer than they want. Stock options often come with complex rules and vesting periods.
Effects On Company Performance
Stock-based compensation can boost employee motivation and focus. It aligns employee goals with company success. This may lead to better productivity and growth. On the other hand, it can dilute existing shareholders’ ownership. Companies must balance rewards with the impact on stock value.
Common Terms To Know
Understanding stock-based compensation means knowing key terms. These terms explain how stock options and shares work. They help employees see the value and timing of their rewards.
Vesting Schedule
A vesting schedule shows when you earn your stock options. You don’t get all options at once. They come over time, often years. You must stay with the company to earn them.
Exercise Price
The exercise price is the cost to buy your stock option. It stays fixed even if the stock price rises. You pay this price to own company shares. It’s also called the strike price.
Fair Market Value
Fair market value is the current price of a stock. It’s what you could sell shares for on the open market. Companies use this value to set option prices. It changes daily with the stock market.

Credit: www.wallstreetmojo.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Stock-based Compensation In Simple Terms?
Stock-based compensation is a payment method using company shares instead of cash. It rewards employees with ownership stakes, aligning their interests with company success and promoting long-term commitment.
How Does Stock-based Compensation Benefit Employees?
Employees gain potential financial growth if the company’s stock price rises. It also offers a sense of ownership and motivates better performance and loyalty.
What Are Common Types Of Stock-based Compensation?
Common types include stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs), and employee stock purchase plans (ESPPs). Each type has different vesting schedules and tax implications.
How Is Stock-based Compensation Taxed?
Tax treatment depends on the award type and timing of exercise or sale. Generally, employees pay income tax on the fair market value when shares vest or options are exercised.
Conclusion
Stock-based compensation helps companies reward employees with shares. It can motivate workers to perform better. Employees gain value if the company grows. This form of pay ties success to effort. Understanding it helps you see its benefits and risks. Always consider how it fits your personal goals.
Clear knowledge makes financial choices easier. Stock-based compensation remains a common tool in many businesses today.