Imagine a technology so powerful that it could crack the strongest digital locks protecting your valuable information. Quantum computing is no longer just science fiction—it’s becoming a real force that could change everything about how we keep data safe.
If you rely on blockchain for security, you need to understand why this new kind of computing might put your digital assets at risk. You’ll discover how quantum computers work, why they pose a threat to blockchain security, and what you can do to stay ahead.
Don’t let your data become vulnerable—keep reading to learn how to protect what matters most.
Credit: www.cyfirma.com
Quantum Computing Basics
Quantum computing is a new type of technology. It uses the strange rules of quantum physics. This makes it very different from normal computers. Understanding these basics helps explain why quantum computing can affect blockchain security.
Quantum Bits And Superposition
Quantum computers use quantum bits, or qubits. Unlike regular bits, qubits can be 0 and 1 at the same time. This is called superposition. It allows quantum computers to process many possibilities at once. This power helps quantum machines solve complex problems faster.
Quantum Gates And Circuits
Quantum gates control qubits like logic gates control bits. These gates change qubits’ states using quantum rules. Gates connect to form quantum circuits. These circuits perform calculations. They work differently from classical circuits, allowing new ways to process information.
Quantum Algorithms
Quantum algorithms use qubits and gates to solve problems. They run much faster than classical algorithms in some tasks. For example, they can break certain codes quickly. This speed poses a risk to current cryptographic methods used in blockchains.
Blockchain Security Fundamentals
Blockchain security is the foundation of trust in digital transactions. It relies on several key technologies to protect data and ensure integrity. Understanding these basics helps reveal why blockchain is seen as secure.
Each part plays a role in guarding against fraud and tampering. These elements work together to keep blockchain networks safe from attacks.
Cryptographic Hash Functions
Hash functions turn data into a fixed string of characters. This string looks random but always matches the original data uniquely. If the data changes even slightly, the hash changes completely.
This makes hashes very useful for checking data integrity. They help verify that no one has altered the blockchain records.
Public-key Cryptography
This system uses two keys: one public, one private. The public key encrypts data, while the private key decrypts it. Only the owner of the private key can access the information.
Public-key cryptography secures transactions and verifies identities. It ensures only authorized users can make changes in the blockchain.
Consensus Mechanisms
Consensus mechanisms help all participants agree on the blockchain state. They prevent fraud by requiring agreement before adding new data. Common methods include Proof of Work and Proof of Stake.
These systems protect blockchain from attacks and ensure its reliability.
Quantum Threats To Cryptography
Quantum computers bring new risks to cryptography. They can solve problems that classical computers cannot handle quickly. This ability threatens the security methods used in blockchains and many online systems.
Quantum threats target the core of cryptographic protection. These include public-key encryption, hash functions, and other cryptographic processes. Each plays a key role in keeping data safe.
Breaking Public-key Encryption
Public-key encryption relies on hard math problems. Classical computers take too long to solve these. Quantum computers use algorithms like Shor’s to solve them fast.
This means quantum machines can break keys that secure blockchain wallets. They can find private keys from public keys quickly. This risk puts digital assets and transactions in danger.
Impact On Hash Functions
Hash functions create unique digital fingerprints for data. They protect blockchain integrity and verify transactions. Quantum computers threaten these through faster collision searches.
Grover’s algorithm cuts the search time for hash collisions. This weakens the security level of hash functions. Blockchains must upgrade hash methods to stay safe.
Quantum Speedup Effects
Quantum speedup means solving certain problems much faster. It changes how cryptographic algorithms perform. Some encryption methods become vulnerable almost instantly.
Speedup impacts key generation, encryption, and signature processes. Cryptography must evolve to resist quantum attacks. Without changes, blockchain security faces serious challenges.
Credit: thequantuminsider.com
Vulnerabilities In Blockchain Networks
Blockchain networks rely on strong cryptography to secure data and transactions. Quantum computing poses new risks by breaking this cryptography. This creates vulnerabilities that could damage blockchain security. Understanding these weaknesses is key to preparing for future threats.
Risks To Transaction Integrity
Quantum computers can solve complex math problems faster. This ability might let attackers change transaction data. Altered transactions could go unnoticed, harming trust in blockchain. Maintaining transaction integrity becomes challenging with quantum threats.
Threats To Wallet Security
Wallets use private keys to protect user funds. Quantum machines can potentially guess these keys quickly. Stolen private keys mean stolen funds. Wallet security faces serious risks if quantum computing advances.
Consensus Protocol Challenges
Blockchain networks use consensus protocols to agree on data. Quantum attacks could disrupt these protocols by speeding up calculations. This may cause network confusion or allow dishonest control. Consensus mechanisms need upgrades to resist quantum risks.
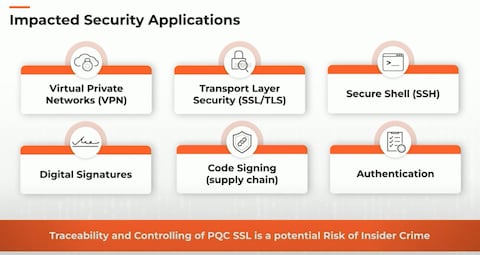
Post-quantum Cryptography Solutions
Post-quantum cryptography solutions aim to protect data from future quantum attacks. Quantum computers threaten current encryption methods. These solutions develop new ways to keep blockchain and other technologies safe. Researchers focus on creating algorithms that quantum computers cannot easily break. This field is growing fast to meet emerging security needs.
Quantum-resistant Algorithms
Quantum-resistant algorithms use math problems hard for quantum computers. Examples include lattice-based, hash-based, and code-based cryptography. These algorithms replace current ones like RSA and ECC. They help protect data by making encryption stronger against quantum attacks. Testing and improving these algorithms is a priority in security research.
Hybrid Cryptographic Approaches
Hybrid approaches combine classical and quantum-resistant methods. This mix ensures strong security today and in the future. It adds layers of protection to data and transactions. Hybrid models allow gradual transition without risking current systems. They provide a safer path until full quantum resistance is achieved.
Standardization Efforts
Standardization groups work to create clear rules for post-quantum cryptography. Organizations like NIST lead the process of selecting secure algorithms. Standards help developers build compatible and reliable security tools. They also guide industries to adopt quantum-safe encryption widely. This ensures a coordinated and effective defense against quantum threats.
Credit: www.paloaltonetworks.com
Adapting Blockchain For Quantum Era
Quantum computing poses a serious challenge to blockchain security. Its ability to solve complex problems fast could break current cryptographic methods. Blockchain networks must evolve to stay secure in the quantum era. Changes in technology and strategy are needed to protect digital assets and data.
Adapting blockchain means redesigning systems to resist quantum attacks. Developers focus on new cryptographic techniques and security layers. Smart contracts also require updates to remain safe and trustworthy. These steps help blockchains keep their integrity and user trust.
Upgrading Protocols
Current blockchain protocols rely on cryptography that quantum computers can crack. Upgrading to quantum-resistant algorithms is essential. These new protocols use math problems that even quantum machines struggle to solve. This upgrade protects transaction data and wallet keys from future threats.
Implementing these protocols takes time and careful testing. Networks must ensure compatibility and smooth transitions. Proper upgrades maintain blockchain speed and efficiency without sacrificing security.
Layered Security Models
Layered security adds multiple defense levels against quantum attacks. Combining classical and quantum-safe methods strengthens protection. This approach reduces the chance that one weak point can be exploited. Each layer works together to guard the blockchain network.
For example, encryption can be combined with biometric verification or multi-signature wallets. These layers create more hurdles for attackers. Layered models improve resilience without major changes to user experience.
Quantum-safe Smart Contracts
Smart contracts automate transactions and agreements on blockchains. Quantum threats put these contracts at risk of tampering or theft. Developing quantum-safe smart contracts means using new cryptographic tools. These tools secure contract code and execution against quantum attacks.
Testing quantum-safe contracts ensures they function correctly and securely. This protects users from fraud and keeps blockchain applications reliable. Quantum-safe smart contracts are vital for future-proof blockchain ecosystems.
Future Outlook And Research
The future of quantum computing and its impact on blockchain security is an active area of study. Researchers focus on how quantum machines might break current encryption methods. They also explore new ways to protect digital data from these threats.
Research aims to prepare blockchain systems for the challenges ahead. It involves improving hardware, assessing security continuously, and working together across fields. These efforts help build stronger defenses against quantum attacks.
Quantum Hardware Advancements
Quantum hardware is evolving quickly. Companies and labs develop more stable and powerful quantum processors. These machines can solve complex problems faster than classical computers. As hardware improves, the risk to blockchain security rises. Tracking these changes helps experts stay prepared.
Ongoing Security Assessments
Experts regularly test blockchain systems against quantum threats. They check if current cryptographic methods remain secure. New algorithms are developed and tested to resist quantum attacks. Continuous assessment ensures timely updates to security protocols. This process helps blockchains stay safe as technology changes.
Collaborative Defense Strategies
Defending blockchain needs teamwork among researchers, developers, and governments. Sharing knowledge speeds up finding solutions. Joint efforts create stronger, quantum-resistant encryption methods. Collaboration also spreads awareness about potential risks. United actions improve overall security against future threats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Quantum Computing’s Impact On Blockchain Security?
Quantum computing can break traditional cryptographic keys used in blockchain. It poses a threat to transaction integrity and data privacy. Quantum algorithms can potentially crack encryption much faster than classical computers. This risk demands new quantum-resistant cryptographic methods to secure blockchain networks in the future.
How Does Quantum Computing Threaten Blockchain Encryption?
Quantum computers use algorithms like Shor’s to solve complex problems quickly. This ability allows them to break widely used cryptographic algorithms such as RSA and ECC. Blockchain relies on these for securing transactions and digital signatures. Therefore, quantum computing threatens blockchain’s fundamental security mechanisms.
Can Blockchain Be Protected Against Quantum Attacks?
Yes, blockchain can adopt post-quantum cryptography to resist quantum attacks. Researchers are developing quantum-resistant algorithms like lattice-based and hash-based cryptography. These methods aim to secure blockchain even if quantum computers become powerful. Upgrading blockchain protocols is essential to maintain trust and security.
When Might Quantum Computers Break Blockchain Security?
Practical quantum computers capable of breaking blockchain may emerge within a decade. Current quantum machines are not yet powerful enough to threaten cryptography. However, rapid advancements suggest preparation is critical. Blockchain networks must evolve proactively to counter future quantum threats.
Conclusion
Quantum computing may change blockchain security soon. It can break current encryption methods easily. This risk pushes developers to find new solutions fast. Quantum-resistant algorithms are under strong research now. The future of blockchain depends on these advances. Staying aware of this threat helps users prepare.
The balance between innovation and security is crucial. Blockchain technology must evolve to stay safe. The challenge is real but not impossible to solve.






