Have you ever wondered how long it would actually take to travel to Mars? If you’re curious about the journey to the Red Planet, you’re not alone.
Getting to Mars isn’t as simple as hopping on a plane—it involves complex science, powerful rockets, and a lot of planning. You’ll discover the real travel time to Mars, why it varies, and what challenges space explorers must overcome. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of what it takes to make this incredible trip.
Ready to find out how long your ride to Mars might be? Let’s dive in.

Credit: www.space.com
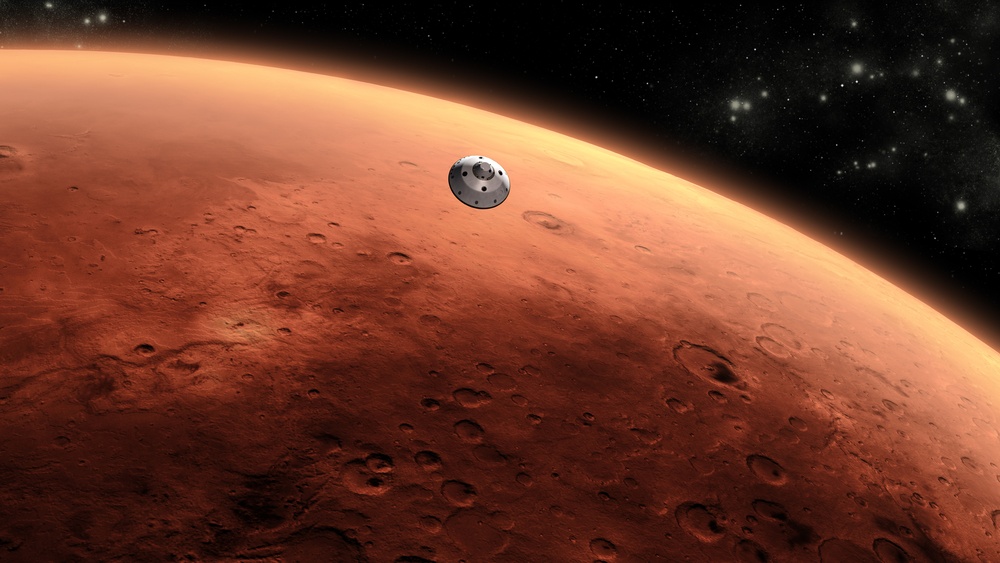
Travel Time To Mars
Travel time to Mars varies widely depending on the mission plan and technology used. Mars and Earth orbit the sun at different speeds and distances. This causes the distance between the two planets to change continuously. Traveling to Mars requires careful timing to use the shortest path and least energy.
Space agencies plan missions during specific launch windows. These windows occur roughly every 26 months when Earth and Mars are closest. The journey speed and route affect the total travel time significantly.
Typical Duration
A typical trip to Mars takes about six to nine months. Most spacecraft follow a path called the Hohmann transfer orbit. This route uses the least fuel by traveling along an elliptical orbit between Earth and Mars. The exact time depends on the spacecraft’s speed and the planets’ positions.
Factors Influencing Journey Length
Several factors change how long the trip to Mars takes. The distance between Earth and Mars varies from 54.6 million km to over 400 million km. Faster spacecraft reduce travel time but require more fuel. Launch windows and orbital paths also play a major role. Advanced propulsion methods could cut travel times in the future.
Current Mission Examples
NASA’s Perseverance rover launched in July 2020 and arrived in February 2021. Its trip took about seven months. The InSight lander reached Mars in roughly six months in 2018. These missions use chemical rockets and Hohmann transfer orbits. They represent the current standard for Mars travel time.

Credit: www.space.com
Orbit Paths To Mars
Traveling to Mars requires choosing the best orbit path. The path affects the time it takes for the spacecraft to reach the red planet. Different orbit paths use different amounts of fuel and time.
Scientists and engineers plan the journey carefully. They pick orbit paths that save energy and ensure safety. Two common paths are the Hohmann Transfer Orbit and Alternative Trajectories.
Hohmann Transfer Orbit
The Hohmann Transfer Orbit is the most common path to Mars. It uses an elliptical orbit that touches both Earth’s and Mars’ orbits. This path uses less fuel than other options.
The spacecraft leaves Earth’s orbit and moves toward Mars along this ellipse. The trip usually takes about 6 to 9 months. Timing is important. Launch windows open about every 26 months when Earth and Mars align well.
This orbit is simple and energy-efficient. Many Mars missions use this path because it balances travel time and fuel use well.
Alternative Trajectories
Alternative trajectories offer faster or different routes to Mars. These paths may use more fuel but reduce travel time. For example, some missions use faster transfer orbits or gravity assists.
Gravity assists use the pull of other planets to change speed and direction. This method can shorten the trip. Other paths use advanced propulsion to speed up travel.
Scientists explore these options to find quicker ways to reach Mars. Future technology could make these trajectories more common and practical.
Future Propulsion Technologies
Traveling to Mars takes months with current rockets. Scientists work on new propulsion methods to cut this time. These future technologies aim to make Mars trips faster and safer.
New propulsion systems use innovative ideas. They can push spacecraft at higher speeds. This can reduce the journey from months to weeks or less.
Photonic Propulsion
Photonic propulsion uses light particles called photons to push spacecraft. Powerful lasers shine on a special sail attached to the ship. The light’s pressure slowly speeds up the spacecraft.
This method needs less fuel than rockets. It can achieve very high speeds over time. Photonic propulsion is still experimental but shows promise for long trips like Mars.
Advanced Rocket Systems
Advanced rockets use new fuel types and designs. Some use nuclear power to generate more thrust. Others combine chemical and electric propulsion for efficiency.
These rockets can carry heavier loads faster. They can shorten the Mars trip by boosting speed and reducing stops. Development continues to improve safety and power.
Potential Time Reductions
New propulsion methods could reduce Mars travel to weeks. Photonic sails might reach speeds much higher than current rockets. Advanced rockets can cut travel time by half or more.
Shorter trips lower risks for astronauts. They reduce exposure to space radiation and other dangers. Faster travel makes Mars missions more practical in the future.
Challenges Of Mars Travel
Traveling to Mars is a huge challenge. The journey is long and dangerous. Space is a harsh environment for humans. Many problems must be solved before people can live there safely. The risks include radiation, life support, and mental health. These challenges shape how missions are planned and how long they take.
Understanding these challenges helps us see why Mars travel is difficult. Each problem needs careful attention. Scientists and engineers work hard to find solutions. The trip to Mars is not just about distance but also survival.
Radiation Exposure
Space has high levels of radiation. Earth’s atmosphere protects us from most of it. On the way to Mars, astronauts face strong cosmic rays. These rays can harm cells and cause cancer. Spacecraft need heavy shielding to reduce radiation risks. Still, some radiation will reach the crew during the trip. Protection is a major concern for long missions.
Life Support Needs
Astronauts need air, water, and food to survive. These supplies must last the whole trip. Recycling systems help save resources. Growing food in space is a goal but not yet common. Equipment must keep the environment safe and stable. Any failure in life support can be deadly. Careful planning is vital for survival on Mars missions.
Health Effects Of Microgravity
Microgravity changes how the body works. Bones lose density and muscles weaken. Blood flow and heart function can also change. Long stays in space can cause vision problems. Exercise helps reduce these effects but cannot stop them all. Astronauts must prepare their bodies for these changes. Returning to Mars’ gravity will require adjustment.
Psychological Stress
Being far from Earth causes mental strain. Isolation and confinement affect mood and behavior. Crew members live in tight spaces for months. Communication delays with Earth add to the stress. Teams train to handle conflicts and loneliness. Mental health support is critical for mission success. Keeping astronauts mentally strong is as important as physical health.
Landing On Mars
Landing on Mars marks one of the most critical moments in any mission. The process demands precise control and timing. Mars has a thin atmosphere that makes landing tricky. Spacecraft must slow down from thousands of miles per hour to a safe landing speed. Success depends on overcoming many challenges during the entry, descent, and landing phases.
Entry, Descent, And Landing Difficulties
The spacecraft first hits Mars’ atmosphere at very high speed. Friction with air creates intense heat. Heat shields protect the craft from burning up. As it descends, parachutes open to slow it down further. The thin atmosphere reduces parachute effectiveness. Rockets often fire to reduce speed just before touchdown. Timing is vital to avoid crashes. Small errors can cause mission failure.
Heavy Payload Challenges
Landing heavy payloads on Mars adds more difficulty. Larger mass means more speed to reduce. Bigger heat shields and stronger parachutes are needed. Rockets must provide more thrust for a gentle landing. The surface of Mars is rocky and uneven. It requires careful site selection to avoid damage. Engineers design landing systems to handle these loads safely.
Reducing Travel Time
Reducing travel time to Mars remains a key focus for space agencies and scientists. Shorter trips mean less risk for astronauts and lower mission costs. Advances in technology and smarter planning play vital roles in making this possible.
Efforts to cut down the travel duration help pave the way for future Mars exploration missions. Understanding these methods offers insight into how humans might reach Mars faster.
Technological Innovations
New propulsion systems aim to speed up Mars travel. Ion thrusters use electricity to push spacecraft efficiently. Nuclear thermal rockets promise more power and faster acceleration. Photonic propulsion, still experimental, uses light for thrust. These technologies could reduce journey time from months to weeks.
Improving spacecraft design also helps. Lighter materials and better fuel storage increase speed and range. Faster travel means less exposure to space radiation for astronauts.
Mission Planning Strategies
Choosing the best launch window cuts travel time significantly. Launching when Earth and Mars are closest saves fuel and time. This event, called opposition, happens roughly every 26 months. Precise timing allows spacecraft to take the shortest path.
Advanced navigation techniques guide spacecraft on efficient routes. Gravity assists from other planets can boost speed without extra fuel. Careful mission design balances speed, safety, and cost.

Credit: science.howstuffworks.com
Frequently Asked Questions
How Long Does It Take For Humans To Get To Mars?
Traveling to Mars takes about six to nine months using current rocket technology. Advanced propulsion could shorten this time.
Can We Get To Mars In 3 Days?
Traveling to Mars in 3 days is impossible with current technology. Typical trips take about 6 to 9 months using existing rockets. Advanced propulsion systems may reduce travel time in the future, but they remain experimental and unproven for manned missions.
Why Can’t We Send Humans To Mars?
Humans can’t travel to Mars yet due to deadly space radiation, long journey risks, limited life support, landing challenges, and high mission costs.
Can Humans Survive In Mars?
Humans cannot survive on Mars unaided due to extreme radiation, thin atmosphere, and lack of breathable air. Advanced technology and life support systems are essential for survival there.
Conclusion
Traveling to Mars takes about six to nine months with current technology. The distance varies as both planets move in their orbits. Scientists use special routes like the Hohmann Transfer Orbit to save fuel and time. Future advances might cut this travel time significantly.
Still, many challenges remain, such as protecting astronauts from space radiation and ensuring their health. Exploring Mars pushes the limits of human technology and endurance. The journey is long, but it opens new frontiers for science and discovery.