If you’ve ever wondered why some web pages pop up instantly on Google while others remain hidden, understanding how Google indexing really works is the key. Imagine your website as a book in a massive library.
Google’s job is to find your book, read it, decide if it’s worth shelving, and then show it to the right reader at the right time. But how does this process actually happen behind the scenes? You’ll uncover the simple yet powerful steps Google takes to crawl, analyze, and store your content.
Knowing this can help you make your pages more visible and get the attention your site deserves. Ready to unlock the secrets of Google indexing? Let’s dive in.
Googlebot And Crawling
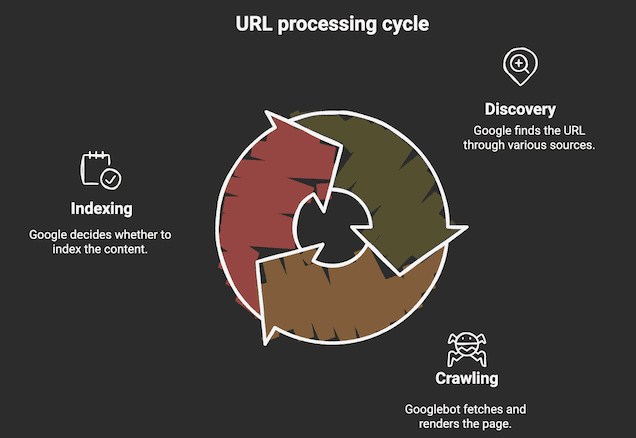
Googlebot and crawling form the foundation of how Google discovers new web content. Googlebot is a software program that scans the internet constantly. It looks for new pages and updates to existing ones. This process is called crawling. Crawling ensures Google stays updated with fresh and relevant information. Understanding how Googlebot works helps website owners improve their site visibility.
Role Of Googlebot
Googlebot acts like a digital spider. It visits web pages and reads their content. It checks text, images, and videos to understand the page. Googlebot decides if the page should be added to Google’s index. Pages that are easy to crawl and have clear content get priority. Googlebot also respects rules set by webmasters to avoid restricted pages.
Following Links
Googlebot finds new pages by following links. It starts with known pages and moves to others by clicking on links. Links act as paths that guide Googlebot across the web. Well-structured links help Googlebot discover pages faster. Broken or missing links can stop Googlebot from finding some pages. Websites with many internal links tend to get crawled more often.
Using Sitemaps
Sitemaps are files that list all important pages on a website. They guide Googlebot directly to pages that need crawling. Sitemaps help Googlebot find pages that are hard to reach by links alone. Submitting a sitemap speeds up the crawling process. It also ensures new or updated pages get noticed quickly. Using sitemaps improves the chance of pages being indexed.

Credit: www.dashclicks.com
Indexing Process
The indexing process is a key part of how Google organizes the web. After crawling discovers a page, indexing starts. Google reads and stores the page’s content in its huge database. This process helps Google decide which pages should appear in search results. The indexing process has several important steps that ensure the best pages show up for users.
Content Analysis
Google examines the text, images, and videos on a page. It looks at keywords and tags to understand the topic. The structure of the page also matters. Clear headings and organized content help Google grasp the main idea. This analysis helps Google figure out what the page is about.
Determining Page Quality
Google checks if the page is trustworthy and useful. It looks for original content and checks for spam or low-value material. Pages with clear, helpful information score higher. Google also considers user experience factors like loading speed. Better quality pages have a better chance to rank well.
Canonical Version Selection
Sometimes, many pages have similar content. Google must pick one “canonical” version to show in results. It chooses the clearest, most complete page to avoid duplicates. This helps keep search results clean and useful. Website owners can also suggest canonical pages using special tags.
Google Index Database
The Google Index Database is the heart of how Google organizes the web’s vast content. It stores information about billions of web pages, images, and videos. This database helps Google quickly find and show the most relevant content to users. Understanding its design reveals how Google manages such a huge amount of data efficiently.
Structure And Scale
The Google Index Database is massive and complex. It holds trillions of web pages from all over the world. The database uses advanced systems to organize this data. Pages are grouped by topics, keywords, and site quality. This structure allows Google to retrieve information fast. The scale of this database is beyond what most can imagine.
Dynamic Updates
The index is not static; it updates constantly. Google bots scan the web 24/7 to find new or changed content. When updates occur, the database refreshes its records. This keeps search results fresh and accurate. Pages that change often get updated more quickly. This dynamic nature helps Google serve the latest information.
Storing Text, Images, And Videos
The database stores more than just text from web pages. It also saves images and videos linked to the content. Each type of media is analyzed for relevance and quality. Google uses special algorithms to understand images and videos. This allows the search engine to show rich results, like thumbnails and previews. All media is linked back to the original page context.
Credit: bloggingx.com
Serving Search Results
Serving search results is the final step in Google’s indexing process. After crawling and indexing, Google must find the best matches for a user’s query. This step happens instantly when someone types a search term. Google looks into its huge database of indexed pages to deliver relevant results.
The process of serving results focuses on speed and relevance. Google aims to show pages that answer the user’s question clearly and quickly. Pages that are not indexed cannot appear in search results. This makes indexing essential for website visibility.
Retrieving From The Index
Google stores billions of pages in its index. When a user searches, Google retrieves data from this index. It does not search the live web at this moment. This speeds up the response time drastically. The system uses advanced algorithms to fetch the most useful pages.
Matching User Queries
Google matches words in the search query with those in the indexed pages. It considers synonyms and related terms to improve accuracy. The search engine also looks at page quality and relevance. It ranks pages based on how well they satisfy the query. User intent plays a key role in this matching.
Visibility In Search
Only indexed pages have a chance to appear in search results. Google decides which pages to show based on relevance and quality. Pages that follow SEO best practices rank higher. Visibility depends on many factors like keywords, site structure, and content freshness. Good visibility drives more traffic to websites.
Crawl Budget Management
Managing crawl budget is crucial for how Google indexes websites. It controls how much time and resources Googlebot spends crawling a site. Efficient crawl budget management ensures important pages get discovered and indexed promptly. It helps avoid wasting resources on low-value or duplicate pages. Understanding how Google allocates and prioritizes crawl budget can improve your site’s visibility in search results.
Allocation Criteria
Google assigns crawl budget based on site size and health. Large sites with many pages get more crawl resources. Sites that load fast and have few errors also receive higher allocation. Freshness matters too; frequently updated sites attract more crawling. Google avoids crawling broken or duplicate pages to save budget. Proper site structure helps Googlebot navigate efficiently.
Prioritizing Websites
Google focuses crawl efforts on sites with strong authority and trust. Well-known, popular sites often get crawled more often. Sites with unique, valuable content rank higher in priority. Google also considers user engagement signals like traffic and backlinks. Sites that follow best SEO practices get better crawl attention. This prioritization helps Google serve the best content to users quickly.
Impact On Indexing
Crawl budget affects how fast new or updated pages appear in search results. Limited budget can delay indexing of important pages. Excessive crawling of low-value pages wastes budget and slows indexing. Optimizing crawl budget improves overall site indexing speed and quality. Proper management ensures Google indexes your most relevant content first. This leads to better visibility and search performance.
Credit: olntools.com
Canonicalization Explained
Canonicalization is a key process in how Google indexes web pages. It helps Google decide which version of a page to show in search results. Many websites have duplicate or similar content under different URLs. Without canonicalization, Google might get confused and split ranking signals between these duplicates. This can lower a page’s visibility and affect user experience.
By using canonical tags, website owners tell Google which page is the “main” or preferred version. This simplifies indexing and improves ranking clarity. Understanding canonicalization is essential for effective SEO and better search performance.
Handling Duplicate Content
Duplicate content appears when the same or very similar content is on multiple URLs. This can happen due to tracking parameters, session IDs, or site structure. Google tries to avoid showing duplicates in search results. Canonical tags point Google to the original page to index.
Google uses canonicalization to group duplicates and treat them as one. This helps keep the search index clean and avoids penalties for duplicate content.
Choosing The Best Version
Google selects the best page version based on quality and relevance. The canonical tag guides Google to the preferred URL. If no tag exists, Google may choose the URL it finds most useful. Site owners should always specify a canonical URL to avoid confusion.
Correct canonicalization ensures that link equity and ranking signals combine on one page. This strengthens the chosen page’s authority and ranking potential.
Effects On Search Rankings
Proper canonicalization improves search rankings by consolidating signals. It prevents splitting of backlinks, social shares, and user engagement metrics. This focused signal helps Google rank the canonical page higher.
Incorrect or missing canonical tags can cause ranking drops. Google may rank a less relevant duplicate or split authority across many URLs. Clear canonicalization supports better indexing and boosts SEO results.
Common Indexing Issues
Common indexing issues can stop your web pages from appearing in Google search results. These problems affect how Google crawls and understands your site. Fixing them improves your site’s visibility and traffic.
Pages Not Indexed
Sometimes Google does not add pages to its index. This means these pages won’t show up in search results. Reasons include new pages not yet crawled or pages with errors. Duplicate content or noindex tags also block indexing. Check Google Search Console to see which pages are missing. Submit sitemaps and fix errors to get pages indexed faster.
Blocked Crawling
Googlebot needs access to your pages to crawl them. If crawling is blocked, pages cannot be indexed. Common blocks are robots.txt rules and meta tags like noindex. Server errors or slow response times can also stop crawling. Ensure your robots.txt file allows crawling. Remove any unintended noindex tags. Test your site with Google’s URL Inspection tool to check for crawl issues.
Content Quality Concerns
Google favors pages with unique and useful content. Thin or low-quality content may not get indexed. Pages with very little text or copied material often get ignored. Content must be clear and relevant to user queries. Add detailed information and avoid keyword stuffing. Improving content quality helps Google understand your pages better and increases chances of indexing.
Tools To Monitor Indexing
Monitoring how Google indexes your website helps ensure your pages appear in search results. It also reveals issues that might block indexing. Several tools give clear insights into crawling and indexing processes. Using these tools regularly can improve your site’s visibility.
Google Search Console
Google Search Console is a free tool from Google. It shows how Google views your website. You can check which pages are indexed and spot errors. The tool sends alerts for critical indexing problems. It also helps submit sitemaps to guide Google’s crawlers.
Crawl Stats Reports
Crawl stats reports reveal how often Googlebot visits your site. They show total crawl requests, response times, and errors. This data helps you understand Google’s activity on your pages. If crawl rates drop, it may signal site issues. Monitoring these stats ensures Googlebot can access your site easily.
Index Coverage Insights
Index coverage insights detail which pages are indexed or blocked. They highlight errors like redirects, noindex tags, or server problems. This report helps identify pages that Google cannot add to its index. Fixing these errors improves your site’s chances of ranking higher. It also prevents important pages from being left out.
Improving Indexing Efficiency
Improving indexing efficiency is essential for making sure Google finds and understands your website quickly. Efficient indexing helps your pages appear in search results faster. It also ensures that Google spends its limited crawl budget wisely on your site. Small changes can lead to better visibility and more traffic.
Optimizing Site Structure
A clear site structure guides Googlebot through your pages easily. Use simple navigation menus and logical categories. Internal links should connect related content. Avoid deep nesting of pages that makes crawling harder. A flat structure helps Google index more pages in less time.
Submitting Sitemaps
Sitemaps act like a roadmap for search engines. Submit an XML sitemap in Google Search Console to highlight important pages. Keep the sitemap updated whenever you add or remove pages. This helps Google discover new content faster. A good sitemap improves crawl efficiency and indexing speed.
Regular Content Updates
Frequent content updates signal that your site is active. Google revisits sites with fresh content more often. Update old posts with new information or add new articles regularly. This keeps your site relevant and encourages faster indexing. Consistency in updates improves your site’s overall crawl frequency.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Does Google Indexing Work?
Google indexing starts with Googlebot crawling web pages by following links. Then, it analyzes and stores content in its database. Finally, Google serves relevant indexed pages to users based on their search queries, making those pages visible in search results.
Why 96.55% Of Content Gets No Traffic From Google?
Most content lacks traffic because it fails to rank due to poor quality, weak SEO, or low relevance to user queries.
Can You See How Many Times Someone Has Googled You?
No, Google does not show how many times someone has searched for you. Search data stays private and anonymous.
How Does Google Decide What Comes Up First?
Google ranks pages by crawling, analyzing content quality, relevance, and user experience. It then indexes and displays the most useful results first.
Conclusion
Understanding how Google indexing works helps websites get noticed. Google uses bots to crawl pages and gather content. It then analyzes and stores this data in its huge index. Only indexed pages can appear in search results. Website owners should focus on quality content and clear structure.
Good links and sitemaps help Google find pages faster. Remember, indexing is key to being visible online. Keep your site updated and easy to navigate. This improves chances of ranking well in Google searches.